
Loading....
Close



Human beings get their food & many resources from plants. The green expanse of the forests, filled with various types of plants, is where we primarily source our raw materials. Plants not only ensure the survival of the human race but also their prosperity, providing us with an abundance of resources that we utilize intelligently to make our lives easy & hassle-free.
Every time we step out, we witness the beautiful greens and a distinct variety of plants with different appearances and functions. That is why we, at JBM Global School recognized as one of the top schools in Noida, encourage our students to visit their nearby garden and see the many different types of plants found in nature.
Plants vary so much from each other due to their differing growth habits and characteristics. Let us learn more about the various categories that plants have been divided into.
Following are some of the main types of plants:

These are small plants that have soft, green & delicate stems with not many branches or any wood tissue. These are easier to uproot from the soil, making them easier to plant in a pot.
It takes just one or two seasons for these to have a complete life cycle. Herbs contain a lot of nutritional benefits. They are often used for medicinal purposes. Mint, rosemary, tomato, paddy, and bananas are some examples of herbs.
Also Read: What is the Daily Routine of a Student?

These are mid-size woody plants that have hard, woody & flexible stems and many branches. Generally, their height ranges from 6m to 10m tall, making them taller than herbs yet shorter than trees.
Shrubs have varying lifespans as per different species. Some common examples of shrubs are rose, jasmine, lemon, tulsi, and henna.
Also Read: What is The Importance of Discipline in Students’ Life?

Big & tall plants with very thick, hard & woody stems (trunk) are called trees. Their trunk (main stem) has many branches attached that bear leaves, flowers, and fruits. However, you will find that not all trees have branches, some are branchless such as coconut trees.
The general lifespan of a tree is very long. They live for several years, some live for decades and few live through centuries as well. You can find trees such as Banyan, mango, neem, cashew, teak, and oak around you.
These are plants with fragile, long & thin stems, which makes them unable to stand upright without support. So, they creep and spread readily on the ground all around. Watermelon, strawberry, pumpkin, and sweet potatoes are common examples of creepers.
Also Read: 7 Types Of Soil On Earth’s Surface

These are more complex than creepers. Similar to creepers, climbers also have long, thin, and weak stems that are unable to stand upright, but when given external support, these grow vertically and are capable of carrying their own weight.
Climbers have special structures known as tendrils that help them climb. Some of the common climbers are pea plants, grapevine, sweet gourd, money plants, and more.

These are the diverse groups of plants that produce flowers for reproduction. They are also known as angiosperms and are crucial in ecosystems for providing food, shelter, and oxygen to animals. Some common examples of flowering plants are roses, lily, hibiscus, and more.
Also Read: How To Avoid Sleep While Studying?

These are the spore-bearing plants that, unlike flowering plants, do not bear flowers or seeds but consist of roots, stems & leaves and usually reproduce sexually through tiny spores and sometimes asexually through vegetative propagation. Some common ferns are Boston fern, Staghorn fern, Holly fern, and more.

Mosses are small, flowerless plants that typically form dense green clumps, often in damp or shady locations. They usually carpet woodland and forest floors. Some of the common examples of mosses are Riccia, Sphagnum, Funaria, Polytrichum, etc.
Also Read: Internet: Its Advantages and Disadvantages

These are the plants that have their parts thickened and fleshy, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions and to cope with the climate they have been presented with. Some common examples of succulents are Cacti, Aloe, Snake plants, ZZ Plants, Jade plants, and more.

These are the plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments – saltwater or freshwater. Aquatic plants, also known as hydrophytes, grow in or near water. They can be emergent, submergent, or floating on water. Some common examples of aquatic plants are water lily, lotus, and water hyacinth.
Also Read: The Role of Science Exhibitions in Schools

These are the plants that can grow as climbers, shrubs, tree-like, and stemless plants and are distinguished by their large, compound, evergreen leaves known as fronds. When palms grow as trees, they are called palm trees. Some common types of palms are coconut trees, date palms, and foxtail palms.

These are the plants that derive some or most of their nutrients from trapping and consuming insects and sometimes animals such as small mammals & birds. Some common examples of carnivorous plants are pitcher plants, Venus flytraps, and cobra lilies.
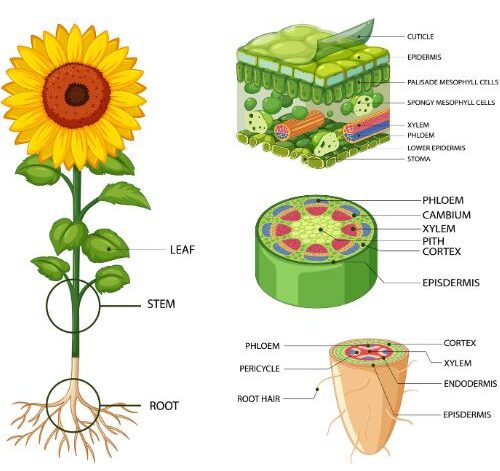
Plants typically have the following parts:
1. Roots – These are the underground part of a plant that absorbs water and minerals and anchors the plant firmly in the soil.
2. Stems – It is the part of the plant above the ground that supports the plant and transports water and minerals from roots to its other parts.
3. Leaves – These are flattened green outgrowth They contain chlorophyll that helps the plants to prepare their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
4. Flowers – The most beautiful and colorful part of a plant, flowers are the reproductive part of a plant, consisting of petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils.
5. Fruits – Fruits are the matured ovary, developed after fertilization. They are pulpy and nutritious.
6. Seeds – It is the plant embryo or ripened ovule that contains food reserves enclosed in a protective outer covering called a seed coat.
7. Buds – It is the part of the plant that develops into a leaf, shoot, or flower. Buds are not yet mature or fully developed.
8. Nodes & Internodes – Nodes are the joints between leaves and stems while internodes are the regions that join two nodes.
9. Cambium – It is a plant tissue from which phloem & xylem grow by division, resulting in secondary thickening in woody plants.
10. Bark – The outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants are called bark. Usually, trees, woody vines, and shrubs contain bark.
11. Petiole – It is the part that attaches the leaf blade to the stem and enables the leaf to twist towards the sun.
Also Read: 6 Reasons Why Constructive Criticism Is Important
12. Blade – Also known as lamina, the leaf blade is the expanded thin, green part of the leaf that conducts photosynthesis.
Plants are incredibly useful to humans in a variety of ways. They provide essential resources, and environmental benefits, and contribute to our overall well-being.
1. Food – They are the ultimate source of food for humans and animals. They provide a wide range of fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds that form the basis of our diets.

2. Oxygen – Through the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the atmosphere which is essential for maintaining oxygen levels.
Also Read: The Significance of Punctuality in The Lives of Students
3. Medicines – Herbs have healing properties and are often used to treat various illnesses and medical conditions.

4. Raw Material – Plants provide materials for building and construction such as wood, bamboo, and fibers. They also contribute to the production of paper, textiles, and other materials that are essential to our daily lives. In this way, they add great economic value.
5. Climate Regulation: Plants utilize carbon dioxide—a significant greenhouse gas—in the process of photosynthesis. This causes a reduction of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, has an indirect cooling effect, and helps regulate the global climate.
Also Read: Top Qualities of a Good Student
6. Fuel – Biomass from plants can be converted into biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel, offering renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. Hence, plants help in energy production.
7. Shade & Shelter – Plants provide shade to humans and animals on hot, sunny days and shelter to the diverse fauna of the region. They are the wildlife habitat of so many living organisms.

8. Aesthetic Value – Plants add life to the modern infrastructure that often seems to be bland, keeping individuals spending time in spaces with flora around, happy, healthy, and creative.
Also Read: What is a Mock Test & How Does it Benefit Students?
9. Erosion Control – Plants bind the soil together with their root system and don’t let it get eroded.
10. Water Filtration – Plants play a vital role in keeping water clean by absorbing carbon dioxide and expelling oxygen.
11. Recreation & Leisure – Trees provide natural settings for picnics, relaxation, and outdoor sports, enhancing recreational experiences and promoting well-being.

12. Cultural And Spiritual Significance: In many cultures, there has been a common belief that God resides in nature. Plant worship as a part of nature is an age-old ritual practiced widely due to the various resources of fertile land, clean water, and purified air we receive from nature.
Also Read: Importance of Co-Curricular Activities for Students
In essence, plants are the foundation of human civilization, providing us with sustenance, materials, medicine, and a healthy environment. Their importance extends far beyond their basic biological functions, shaping various aspects of our lives and the world we inhabit.
It is always recommended to be surrounded by nature and that is why people keep house plants, plant a garden, keep pots of different kinds of plants on their balconies, and take nature walks to admire the surrounding green beauty and adopt sustainable development practices.
JBM Global School emphasizes the significance of conserving plant life through educating the students about the importation of afforestation in today’s world. It is one of the best schools near Sector 137 Noida that puts major stress on sustainability for a greener tomorrow.
The 5 main types of plants are herbs – small plants with delicate stems, shrubs – medium-sized plants with woody stems, trees – tall plants with thick trunks, creepers – plants with fragile stems that creep on the ground, and climbers – the plants with weak stems that tend to grow vertically with support.
Here are the 10 uses of plants –